The female orgasm is an intriguing phenomenon from a scientific perspective, involving a complex series of physiological and neurological processes. In this article, we will scientifically examine what happens in a woman's body during orgasm and discuss various types of female orgasms.
The female orgasm is an intriguing phenomenon from a scientific perspective, involving a complex series of physiological and neurological processes. In this article, we will scientifically examine what happens in a woman's body during orgasm and discuss various types of female orgasms.
Orgasm as a Physiological Response
The female orgasm is the climax of a series of physiological and neurological events that occur during sexual arousal. During orgasm, the body goes through different stages, involving the nervous system, the circulatory system, and other physiological aspects.
Role of the Nervous System
The nervous system plays a key role in orgasm. During sexual arousal, the brain sends signals through the nervous system, causing the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, oxytocin, and endorphins. These chemicals contribute to the sense of pleasure and well-being associated with orgasm.
The Phases of Orgasm
The female orgasm is often divided into four main phases:
-
Excitement: During this phase, there is an increase in blood flow to the genital area, causing the clitoris to become erect and vaginal lubrication to occur. This phase is a preparation for orgasm.
-
Plateau: Sexual tension continues to build until it reaches a critical point known as the "plateau."
-
Orgasm: During this phase, rhythmic contractions of the pelvic muscles occur, involving the uterus and vagina. These contractions are often accompanied by an intense feeling of euphoria.
-
Resolution: After orgasm, the body gradually returns to its resting state, with the heart and breathing returning to normal.
The Different Types of Female Orgasms
Women can experience various types of orgasms, often linked to the stimulation of different erogenous zones:
-
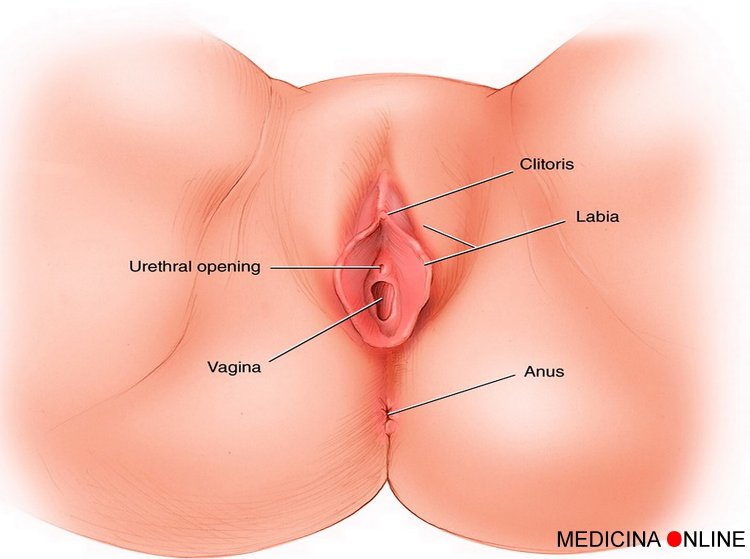
Clitoral Orgasm: This is often the most common type and is associated with direct or indirect stimulation of the clitoris.
-
Vaginal Orgasm: It occurs with vaginal penetration and stimulation of the G-spot, offering a deeper sensation.
-
G-Spot Orgasm: The G-spot is a sensitive area inside the vagina, and stimulating this area can lead to intense orgasms.
-
Brain Orgasm: Orgasms can also be achieved through mental or emotional stimulation, such as intense erotic fantasies.
-
Mixed Orgasm: This involves the simultaneous stimulation of multiple pleasure areas, such as the clitoris and the G-spot.